Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to JavaScript Data Types
JavaScript data types are the fundamental building blocks of any JavaScript program. They define the kind of data you can store and manipulate, allowing you to build effective and dynamic applications. Understanding JavaScript data types is crucial for writing clean, maintainable, and bug-free code.
In this post, we’ll explore five essential data types in JavaScript:
- Numbers
- Booleans
- Strings
- Characters
- Arrays
You’ll learn how each type works, see practical examples, and understand when to use them in real-world applications. By the end, you’ll have a solid foundation to confidently work with JavaScript data types in your projects.
Numbers
Numbers in JavaScript can represent both whole numbers and decimals. JavaScript uses a single Number type to handle integers and floating-point numbers. They are essential for calculations, counting, indexing arrays, or any logic that requires numeric operations.
let age = 35; // integer
let weight = 75.5; // floating-point number
// arithmetic operations
let sum = age + 5;
let product = age * 2;
let quotient = weight / 2;
console.log(sum, product, quotient); // 40 70 37.75
Numbers are versatile and appear in everything from simple arithmetic to complex algorithms. For more on JavaScript numbers, see JavaScript Numbers – MDN.
Booleans
The Boolean data type represents logical values: true or false. Booleans are vital for decision-making, controlling program flow, and comparing values.
let isRaining = true;
let hasUmbrella = false;
// logical operations
console.log(!isRaining); // false
console.log(isRaining && hasUmbrella); // false
console.log(isRaining || hasUmbrella); // true
// conditional statements
if (isRaining) {
console.log("Take an umbrella!");
} else {
console.log("Enjoy the sunshine!");
}
Booleans are also used in loops and conditionals to control program logic. Learn more at JavaScript Booleans – MDN.
Strings and Text
Strings are sequences of characters used to store text. JavaScript strings can be enclosed in single (') or double (") quotes, and they support many operations like concatenation, slicing, and interpolation.
Common String Operations
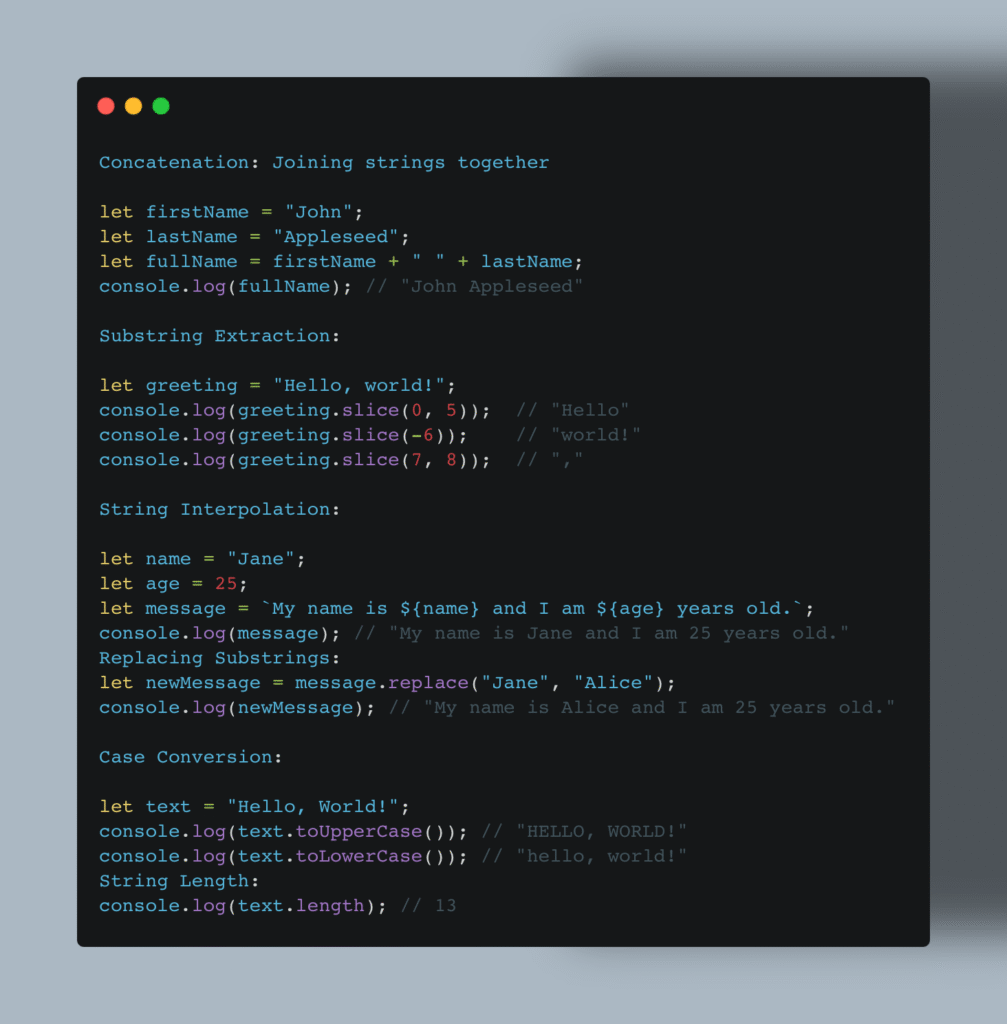
Strings are used extensively for displaying messages, handling user input, or processing text. For a deep dive, check JavaScript Strings – MDN.
Characters
JavaScript does not have a separate character type like some other languages; individual characters are simply strings of length one. You can access characters in a string using indexing:
let fullName = "John";
let firstInitial = fullName[0];
console.log(firstInitial); // "J"
// iterate over each character
for (let char of fullName) {
console.log(char);
}
Characters are often used in text processing, parsing input, or iterating over strings.
Arrays and Lists
Arrays are ordered collections that can hold multiple values of any type. They are one of the most versatile data types in JavaScript, forming the basis for complex structures like stacks, queues, and matrices.
let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"];
// accessing elements
console.log(numbers[0]); // 1
console.log(fruits[2]); // "cherry"
// modifying arrays
fruits.push("date"); // add to end
fruits.pop(); // remove from end
fruits.unshift("kiwi"); // add to start
fruits.shift(); // remove from start
// iterating over arrays
for (let fruit of fruits) {
console.log(fruit);
}
Arrays are critical for managing collections of data, and they work seamlessly with loops and higher-order functions like map, filter, and reduce. See JavaScript Arrays – MDN for more examples.
Tips for Mastering JavaScript Data Types
- Always use meaningful variable names to improve readability.
- Prefer
constfor values that won’t change andletfor mutable data. - Test different operations on numbers, strings, and arrays to understand behavior.
- Combine data types in small projects, such as a to-do list app or a simple calculator.
Conclusion
By understanding JavaScript data types, you now have the foundation to write efficient and maintainable code. Numbers, Booleans, Strings, Characters, and Arrays are the building blocks that power every program.
To expand your knowledge further, check out our detailed guide on JavaScript Variables and Constants — 13 Examples Made Simple for Beginners. Learning how variables, constants, and data types work together will help you write even cleaner and more powerful code.
Happy coding!


